Highlights
- Google’s new earbud technology utilizes APG to accurately monitor heart rates.
- APG-enabled earbuds provide inclusive health tracking, unaffected by skin tone or ear seal.
- The research indicates a median error of under 3.5% for heart rate and variability measures.
- This innovative approach offers a seamless integration of health monitoring into daily wearables.
In the realm of wearable technology, Google has unveiled a pioneering approach that might soon allow earbuds to monitor heart rate.
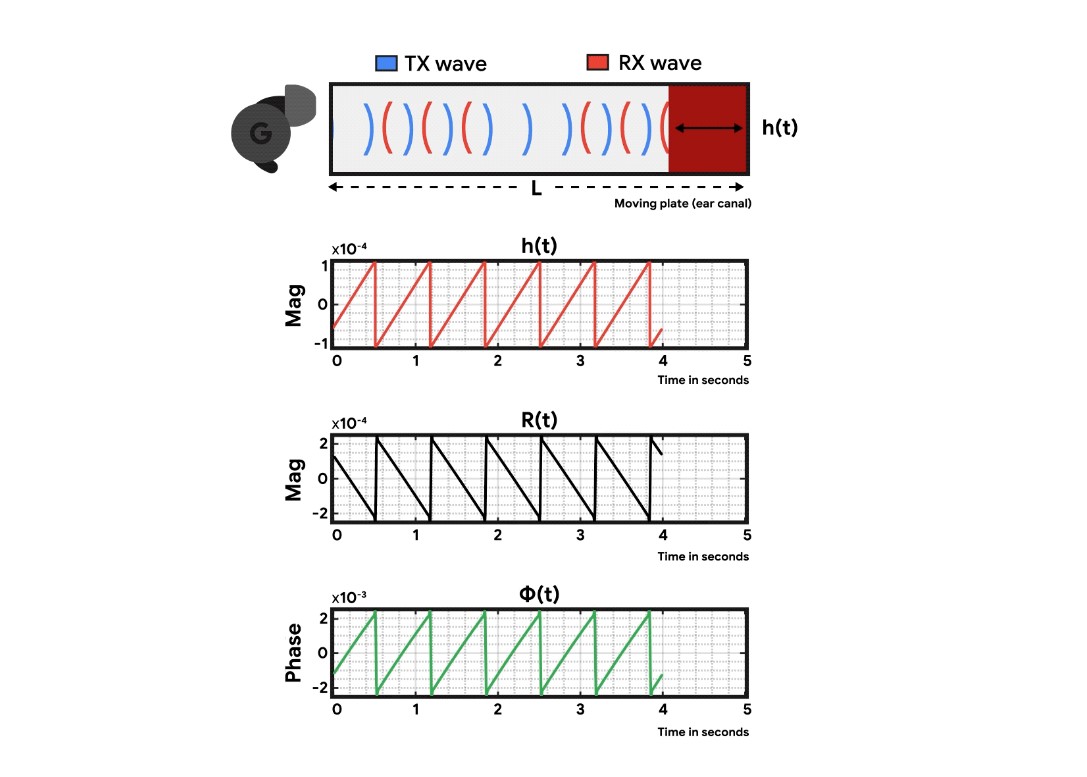
Delving into the field of Audioplethysmography (APG), Google’s researchers have developed a method that employs sound waves to gauge the volume changes in the circulatory system, stepping beyond the typical PPG sensors embedded in most smartwatches.
Bridging the Gap in Health Tech with APG
Despite the widespread adoption of smartwatches equipped with heart rate sensors, a significant demographic either sticks with traditional wristwatches or forgoes them entirely.
This gap in continuous health monitoring is addressed by Google’s APG technology, which can be integrated into earbuds, catering to individuals who prefer not to wear a watch.
With the advent of more advanced Active Noise Cancellation (ANC), transparency modes, and AI, earbuds are increasingly worn for various purposes, including exercise and relaxation.
Google’s research, presented at MobiCom 2023, introduces an active in-ear health sensing method that enables ANC earbuds to measure heart rate and heart rate variability without the need for extra sensors, thus conserving battery life.
Ensuring Accuracy and Safety
The robustness of this system is highlighted by its resilience to motion artifacts and its adherence to safety standards.
Google’s innovative approach ensures the functionality of ANC earbuds as health monitors, unaffected by the fit of the earbuds or the user’s skin tone.
A model has been created by Google to convert the acoustic feedback into accurate heart rate and heart rate variability readings, unaffected by factors such as ear canal size and imperfect earbud seal.
The method was perfected through a multi-tone calibration technique that fine-tunes the frequency used for capturing the heart rate, ensuring high-quality pulse waveform signals.
Research, involving 153 participants, has shown that the APG system devised by Google maintains a median error rate of 3.21% for heart rate and 2.70% for heart rate variability, standing in comparison with FDA-approved devices like the Masimo MightySat Rx and Nonin 9560 Onyx II.
Healthier Future with Hearables
Traditional PPG and ECG sensors, which have been the norm in health-monitoring devices, are often deemed too cumbersome for everyday earbuds due to the added weight and cost.
Google’s research suggests that their APG technology could soon provide a more practical and user-friendly approach to integrating health monitoring into our daily wearables.
This innovative leap by Google is set to enhance the utility of hearables, merging the spheres of health monitoring with entertainment and communication, without adding the burden of additional devices.
FAQs
How does Google’s new earbud technology work to monitor heart rate?
Google’s ANC earbuds employ Audioplethysmography (APG), a technique using sound waves to detect blood volume changes in the ear, allowing for the monitoring of heart rate and heart rate variability without the need for additional sensors.
What makes APG a preferable method for heart rate sensing in earbuds?
APG technology is not influenced by skin tone, ear canal size, or ear seal quality, ensuring a more inclusive and reliable health tracking system. It also operates safely within sound regulation limits, preserving hearing safety.
What were the results of Google’s research on APG in earbuds?
Google’s studies showed APG to have a median error rate of 3.21% for heart rate and 2.70% for heart rate variability, demonstrating high accuracy in comparison to FDA-approved heart rate monitoring devices.
Why is APG considered more practical than traditional sensors for earbuds?
Traditional heart rate sensors like PPG and ECG add significant cost, complexity, and weight to earbuds. APG requires no extra sensors, keeping earbuds lightweight and cost-effective while providing accurate health data.
